Figure 1.

Figure 2.
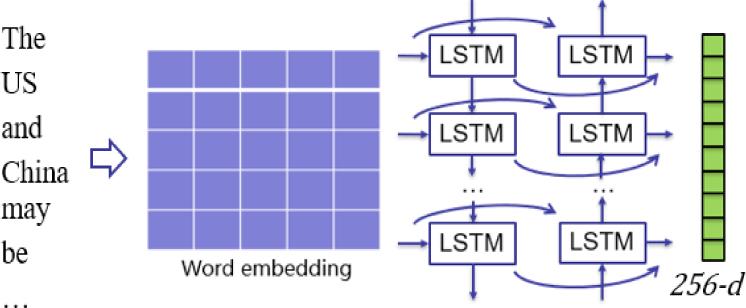
Figure 3.
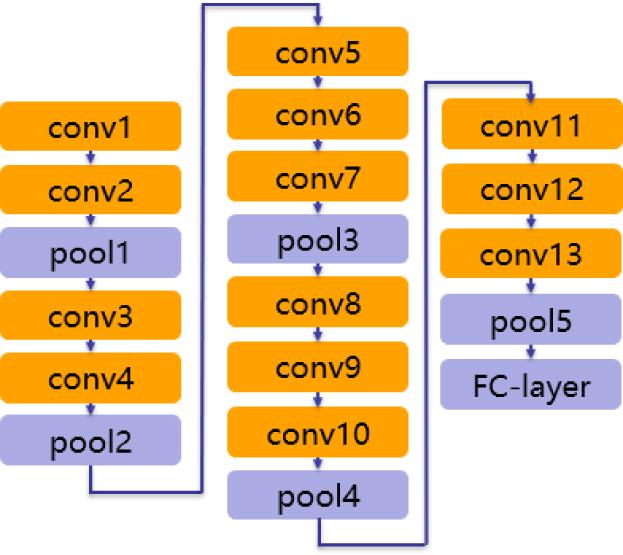
Figure 4.

Figure 5.
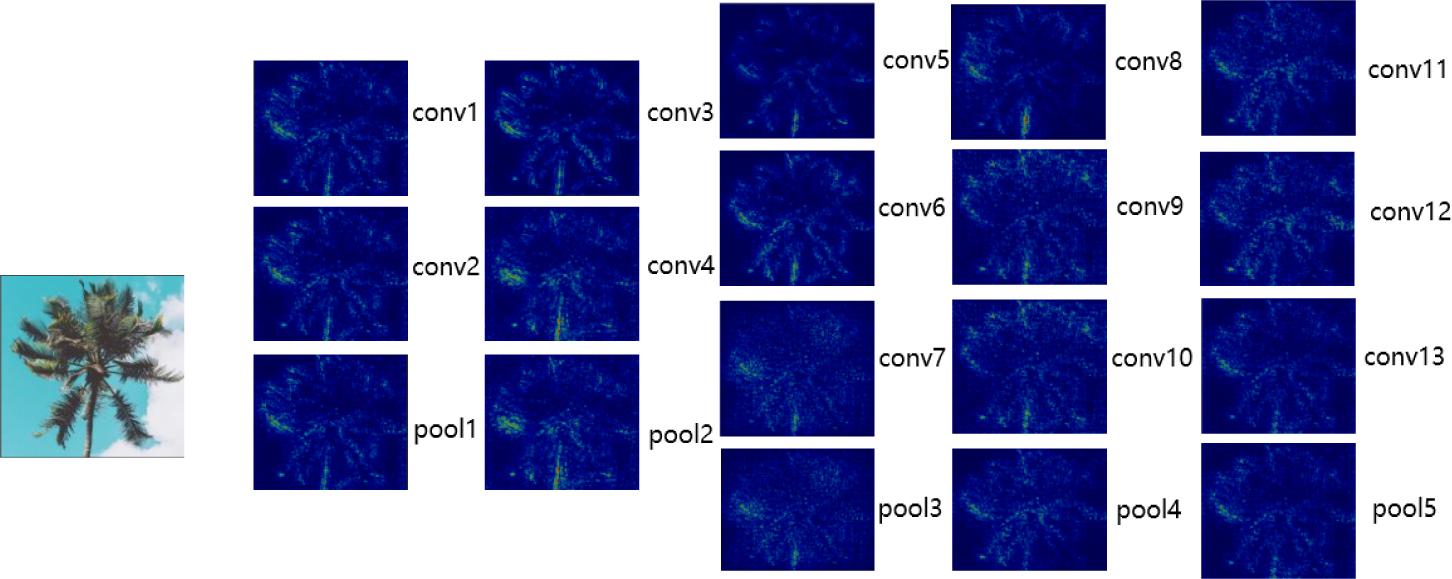
Figure 6.
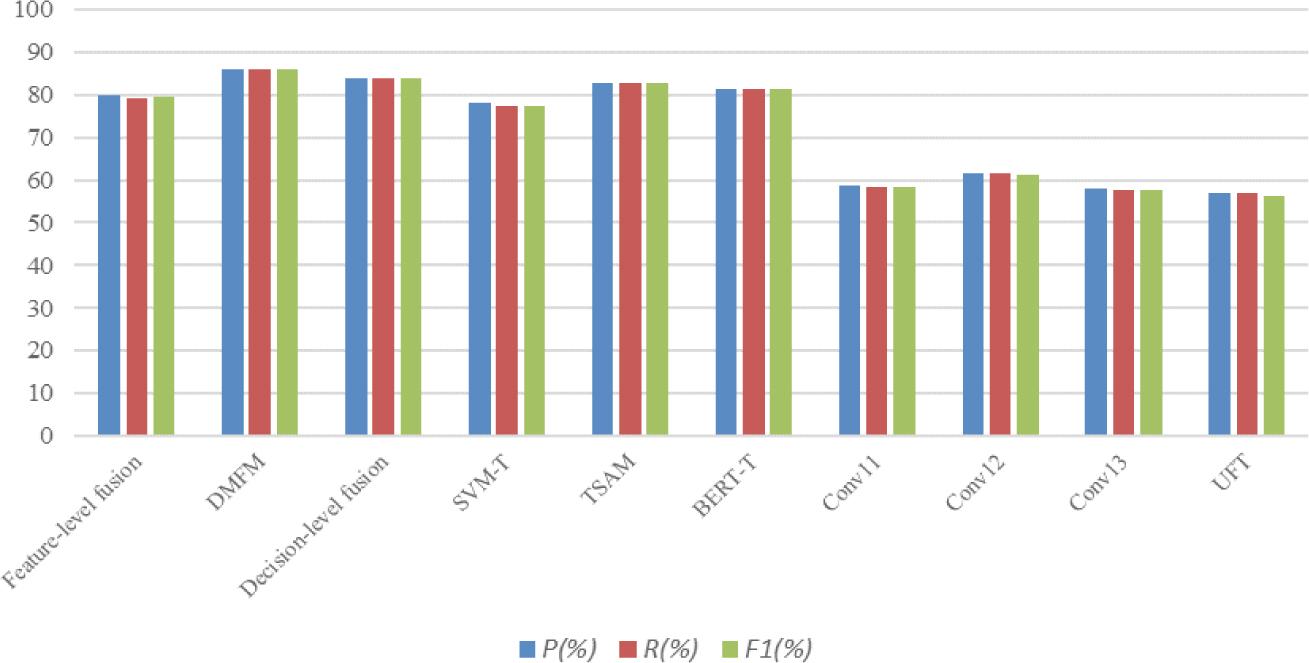
Figure 7.

Figure 8.

Figure 9.
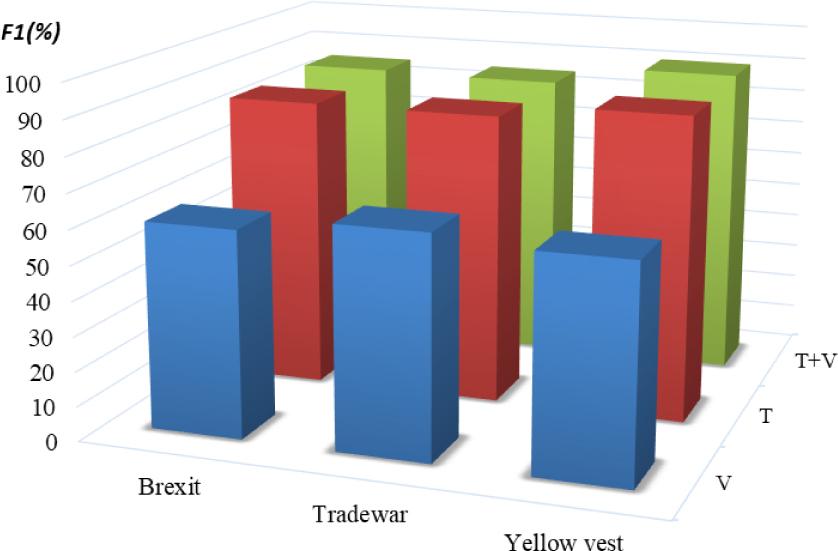
Figure 10.
An instance of Weibo dataset
| Images | Texts (translated) |
|---|---|
| Bauhinia in front of the window: “Typhoon Mangosteen” violently cracked its spine, but still couldn’t hide its charm |
The first-round annotation results of Weibo dataset
| 2-person consistency | 3-person consistency |
|---|---|
| 2003 | 1905 |
An example of multimodal posts on SMPs during public emergencies
| Image | Text |
|---|---|
| On the day of the “Bus Crash”, I also took on a bus in the urban area of Chongqing. As long as one passenger on the bus came out to stop that, it wouldn’t happen today. Rest in peace. |
The first-round annotation results of Twitter dataset
| 2-person consistency | 3-person consistency |
|---|---|
| 2,961 | 2,703 |
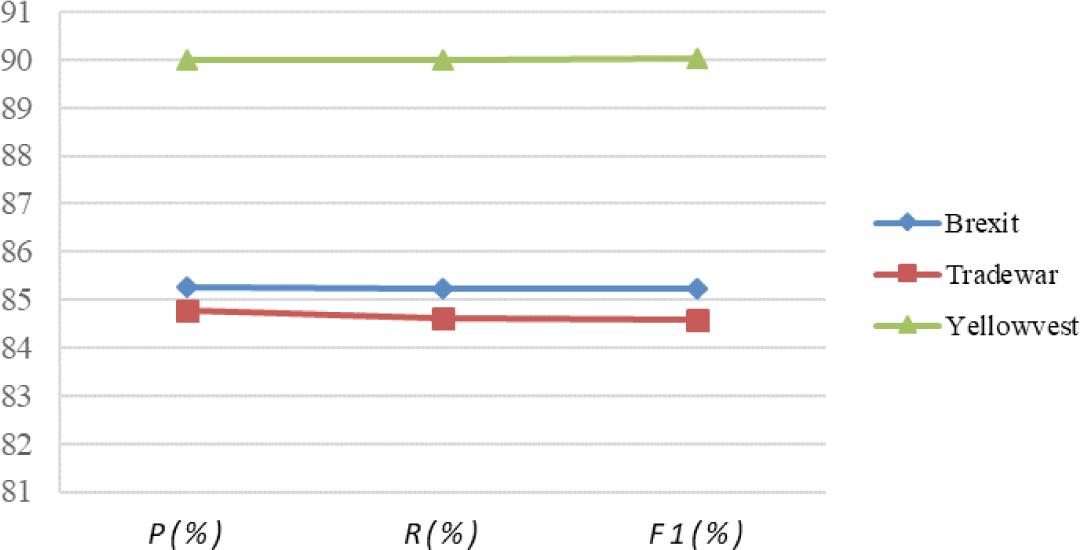
The results of DMFM_conv11, DMFM and DMFM_conv13
| Model | P(%) | R(%) | F1(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DMFM conv11 | 84.701 | 84.742 | 84.695 |
| DMFM | 85.865 | 85.915 | 85.881 |
| DMFM conv13 | 84.266 | 84.272 | 84.118 |
An example of Twitter dataset
| Images | Texts |
|---|---|
| The US and China may be nearing a trade deal. That won’t stop the global economic slowdown |
The results of different multimodal sentiment analysis models
| Model | P(%) | R(%) | F1(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feature-level fusion | 79.903 | 79.288 | 79.496 |
| DMFM | 85.865 | 85.915 | 85.881 |
| Decision-level fusion | 84.010 | 83.960 | 83.936 |
The final annotation results of Twitter dataset
| Positive | Neutral | Negative |
|---|---|---|
| 1,406 | 1,148 | 1,190 |
The results of different textual sentiment analysis models
| Model | P(%) | R(%) | F1(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SVM-T | 78.107 | 77.494 | 77.465 |
| TSAM | 82.760 | 82.864 | 82.750 |
| BERT-T | 81.333 | 81.153 | 81.227 |
The final annotation results of Weibo dataset
| Positive | Neutral | Negative |
|---|---|---|
| 712 | 768 | 649 |
The results of different visual sentiment analysis models
| Model | P(%) | R(%) | F1(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| UFT | 57.051 | 57.042 | 56.357 |
| Conv11 | 58.906 | 58.227 | 58.228 |
| Conv12 | 61.507 | 61.502 | 61.226 |
| Conv13 | 57.861 | 57.512 | 57.625 |
The results of Twitter public emergency dataset, where T represents text and V represents image_
| Model | P(%) | R(%) | F1(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | 83.407 | 83.482 | 83.386 |
| V | 62.336 | 61.867 | 60.934 |
| T+V | 86.463 | 86.400 | 86.401 |